Feathered image source flickr
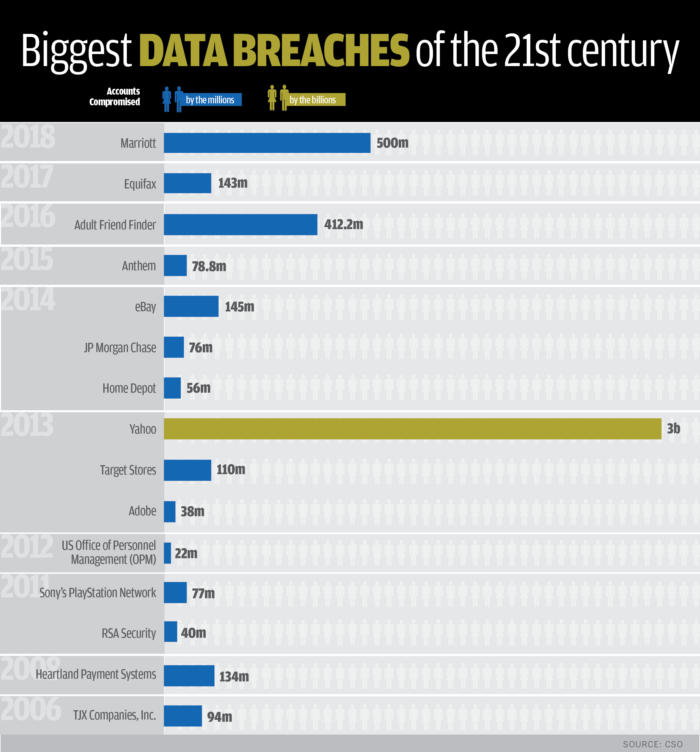
With data breaches and hacks occurring with alarming frequency around the world, governments are taking action to protect their data and the data that belongs to their businesses and private citizens.
The measures that they use look different from one country to the next. With the technology that is used to infiltrate networks and computers constantly evolving, it follows that the law and the measures that are used to protect data must evolve as well.
The Problem
Every country keeps a staggering amount of data. This includes governments, businesses and ordinary citizens. Not so long ago, much of this data was kept in paper files. Stealing the information contained in paper files was complicated. A thief might have to break into a building, circumventing any security systems, and then rifle through reams of paper to find useful data.
Essentially, the thief had to be on the scene in order to do the crime. The prevalence of computers, networks and the Internet has changed all of that. Now, a cyber attack can be orchestrated from down the street or on the other side of the globe.
Organisations and government entities are keeping more information as well. They possess vast databases that are treasure troves of data. Thieves might find social security numbers, birth dates, contact information, credit card numbers, bank account numbers, passwords and much more in one convenient location.
Of course, the criminal still has to “break in” to the system that holds the data, they just don’t use lock picks anymore. Now, they use a range of high-tech equipment to steal staggering amounts of data and money in the blink of an eye.
How Are Nations Responding to Cybersecurity Threats?
The response to these threats is varied across the globe. Some places, like the U.S., have enacted several laws to protect data privacy. The EU has taken a different approach, choosing to enact the GDPR in an effort to put more control back into the hands of consumers. India’s efforts are different still. They are a bit behind the curve when it comes to protecting data.
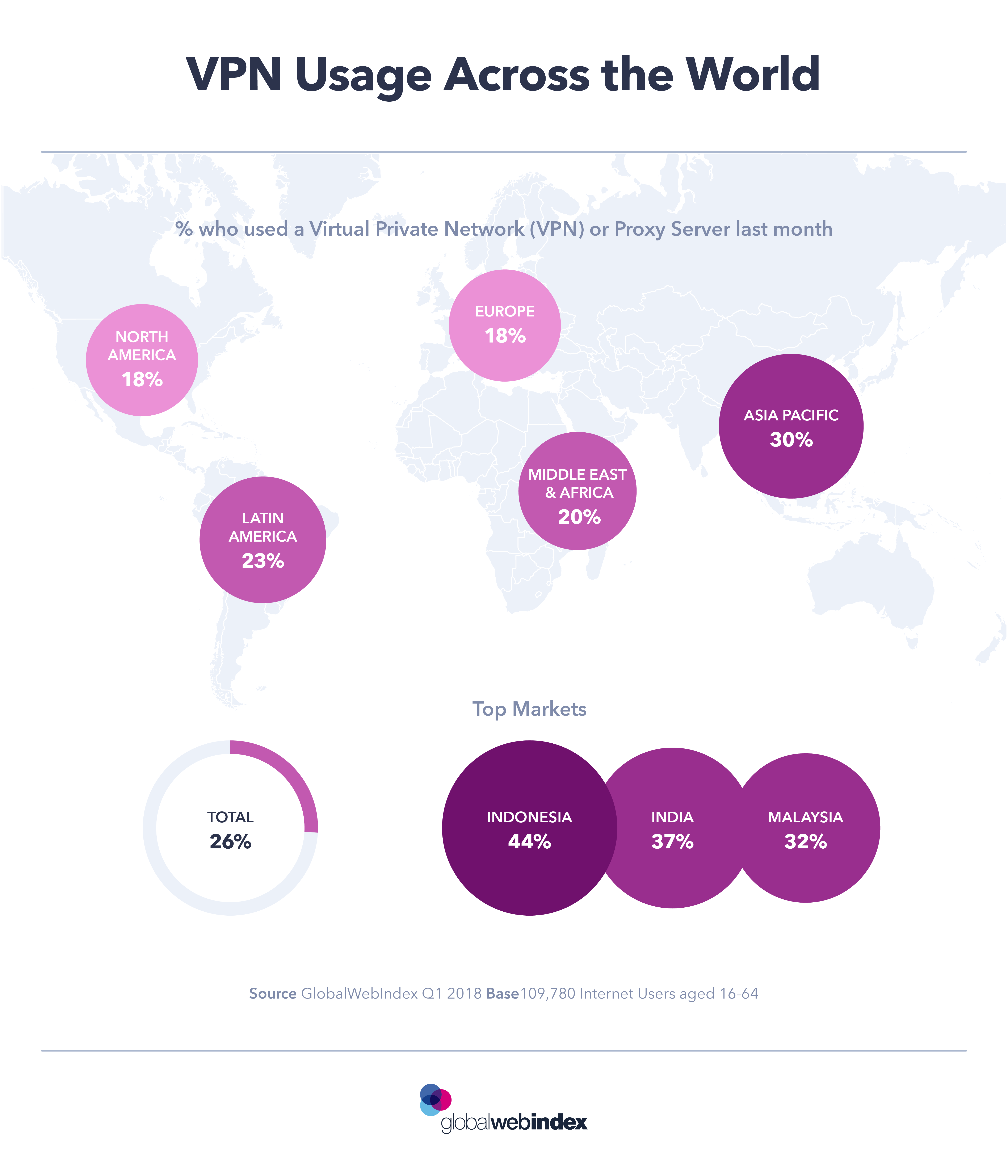
Understanding the various approaches to data protection laws around the world may help individuals to realize that their government doesn’t always know best when it comes to protecting private information. In most cases, it is wise for individuals to protect themselves with measures that might include a VPN.
A VPN is an easy and effective method by which a person’s IP address may be hidden. It makes it look as if this user is in a different location than where they actually are. Best of all, a VPN makes it impossible for anyone to track the user’s movements online.
This makes for an anonymous experience and makes the user far less susceptible to hacks, brute force attacks and other cyber crimes. Unfortunately, not enough people are using VPNs as there are quite a few countries that have banned their use
Data Protection Laws in Australia
Australia has taken an interesting and somewhat effective approach to protecting data. Known as a co-regulatory model, it involves the government and industries working together to come up with and enforce appropriate regulations.
In addition, Australia has established centers for sharing cyber threats across the nation. The effort includes an online portal that helps to collect intelligence and improves the government’s ability to respond to problems. Australia also has a Cyber Security Research Growth Centre, which has a primary aim of developing new products that detect and respond to cyber crime.
The Federal Privacy Act of 1988, which has been amended recently, is the primary law governing data privacy and protection across Australia. Under the law, certain businesses are required to comply with regulations concerning what data they gather, how it is used and how they respond when a breach occurs.
The EU’s General Data Protection Regulation
Known as the GDPR, this law came into effect in 2018, giving citizens of the EU greater control over their personal data and how it’s used. The law requires organizations of all sizes to comply with certain regulations for the protection of data, particularly data concerning individuals. Among the regulations are guidelines for what information can be gathered and ensuring that citizens have given informed consent for the gathering and use of that data. Citizens also have increased rights to be informed whenever a breach of any magnitude has occurred.
Data Protection in the U.S.
Rather than have a single, unifying law like Australia or the EU, America has a slew of laws that pertain to the protection of data. In addition to the federal laws, American states have enacted hundreds of more such pieces of legislation.
As an example of U.S. data protection, the country has an agency called the Federal Trade Commission, or FTC. Most companies and organizations in the U.S. may be penalized by the FTC if they engage in deceptive trade practices. In recent years, this authority has been used against businesses that fail to implement appropriate security measures for data.
India’s Data Protection Laws
To date, India does not have any legislation that is specifically aimed at protecting data. However, they do have the Information Technology Act, 2000. The law is intended to apply to all records whether they are electronic or not.
Additionally, the IT Ministry adopted a set of Information Technology Rules in 2011. These rules defined how could collect, process and store data that is collected from citizens. Overall, India’s data protection laws are considered far less robust than the law that have been enacted in Australia, the EU and the U.S.
How You Can Protect Yourself
Data protection laws around the world are still in their early stages. In many respects, they are not developed or enforced enough to provide a truly safe atmosphere for data. This leaves ordinary citizens with the need to protect themselves. The first step is education, knowing exactly how valuable your data is and protecting it.



